|
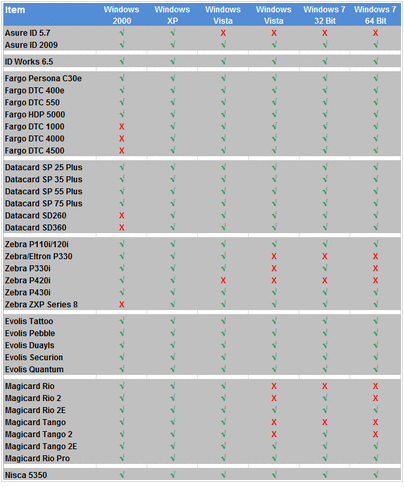
This week's post is a quick tip related to operating systems and ID badge printers. Many organizations are moving over to a Microsoft Windows 7 Operating System.
This transition may directly affect your ID card printing system. Before your organization makes the switch check to see if your ID badge printer will work with Windows 7. If your printer is not on this list, please e-mail me your printer model and we can check the compatibility. If you are changing your operating system to Windows 7, please keep this in mind:
0 Comments
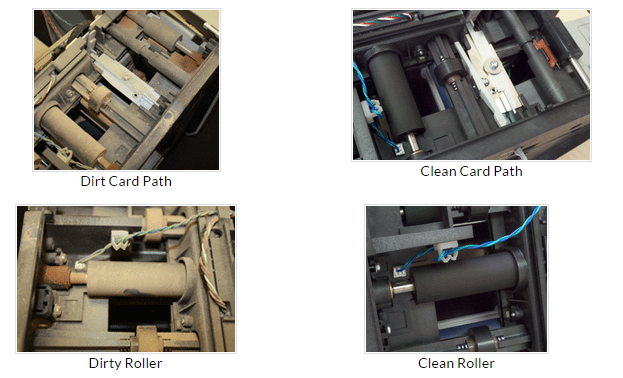
Why Should I Tune-Up my Printer? Your ID printer needs to be able to print on a consistent basis, day in and out. We have all had scenarios where an unforeseen amount of cardholders come at the same exact time needing a card, only to have the printer stop working and have to deal with the frustration of not being able to offer the service we would like. Finding time to have your printer tuned-up can be difficult; however the benefits far outweigh the risks of not getting regular maintenance. Here are just a few of the key steps that should be included in an ID Printer Tune-up:
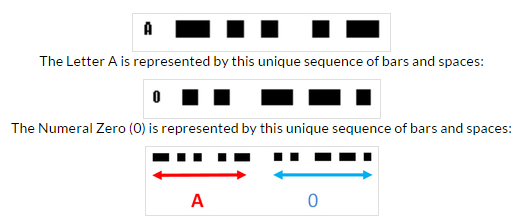
Request a tune-up today How do barcodes work? Barcodes work by having combinations of black bars or dots and spaces. Each barcode type has its own unique language or format. The most common bar code type is one-dimensional bar codes (1-D) which are a series of black bars. When a barcode is swiped or scanned the reader directs some kind of light toward the black bars and spaces and then measures the reflection of light back to the reader. When light is directed at white spaces it reflects the light while light is absorbed by black bars. In this way the reader can determine if it is passing over a black bar (no reflection) or a white space (reflection). The reader can also sense the width of the bars or the spaces. With the basic concept of being able to read bars and spaces and their respective widths, formats have been constructed that assign a character (example 1-9, A-Z, etc) to a unique combination of bars and spaces. The following are two examples of how a common 1-D format type, called Code 39 uses this basic principal of unique sequences of bars and spaces to present a single character: By stringing these unique sequences together you can form multiple characters or numbers. For example "A0" would be as follows:
This simple set of concepts is used to create dozens of different bar codes types for multiple applications. |
Categories
All
Archives
July 2020
|
WE'RE HERE TO HELP.
|
ColorID has spent over 24 years serving the ID Industry with top-level sales and support to build the ultimate trust with every customer.
|
|
|
|